Introduction Digital marketing has become an essential tool for businesses of all sizes. Whether...
Digital Marketing
PPC (Pay-Per-Click Advertising) – A Comprehensive Guide
In the digital marketing world, one of the most effective methods for driving immediate traffic to...
Email Marketing: A Comprehensive Guide
Email marketing is one of the most powerful tools for businesses and organizations to reach their...
Social Media Marketing – A Comprehensive Guide
In today’s digital age, social media marketing has become an essential tool for businesses...
Content Marketing – A Complete Guide to Engaging Your...
In the modern digital era, businesses face an overwhelming challenge: capturing and retaining the...
SEO (Search Engine Optimization)- A Complete Guide
Search Engine Optimization, commonly known as SEO, is a fundamental aspect of digital marketing...
Hello world!
Welcome to WordPress. This is your first post. Edit or delete it, then start writing!
Online Earning
Earn Money Online: Complete Beginner to Intermediate Guide
Introduction Many people today want to Earn Money Online because it offers flexibility...
Understanding Affiliate Programs – A Comprehensive Guide
In the digital age, businesses are constantly seeking new ways to increase sales, reach wider...
Digital Marketing – Transforming the Way Businesses Connect
In today’s fast-paced world, businesses are constantly seeking innovative ways to reach their...
Freelancing – The Modern Way to Work
Freelancing has transformed the way people work in the 21st century. Unlike traditional jobs...
Passive Income – Building Wealth While You Sleep
In today’s fast-paced world, most people work tirelessly from 9 to 5, exchanging their time for...
Work from Home – The Modern Way of Working
In recent years, the concept of working from home has transformed from a rare perk to a mainstream...
Technology News
Tech Trends 2026: Future Innovations Changing the Digital World
Introduction Technology is changing faster than ever, and Tech Trends 2026 are expected to shape...
Tech Innovations – Shaping the Future of Our World
Technology is evolving at an unprecedented pace, transforming every aspect of our lives. From the...
Understanding Software Updates – Importance, Types, and...
In today’s digital era, software is the backbone of nearly every device we use, from computers and...
Cybersecurity – Protecting the Digital World
In today’s digital era, cybersecurity has become one of the most critical aspects of both...
Gadgets – Shaping the Way We Live, Work, and Play
In today’s fast-paced world, gadgets have become an integral part of our lives. From the moment we...
AI (Artificial Intelligence) – Transforming the Modern...
Artificial Intelligence, commonly known as AI, is no longer a concept confined to science fiction...
Web Development
Web Development Tutorials for Beginners and Intermediate Learners
Introduction Web Development Tutorials are a great way to learn how websites and web applications...
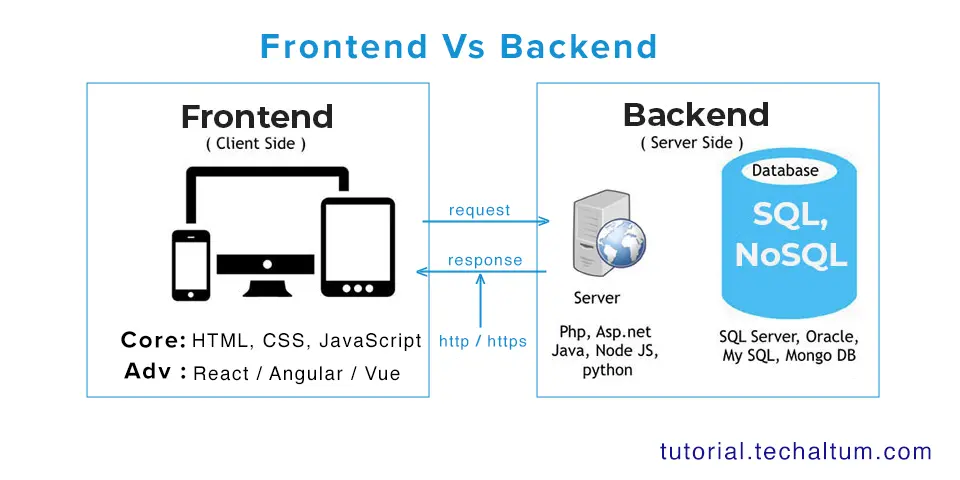
Front-end vs. Back-end – Client-side vs. Server-side...
In the world of web development, two terms are frequently mentioned: front-end and back-end...
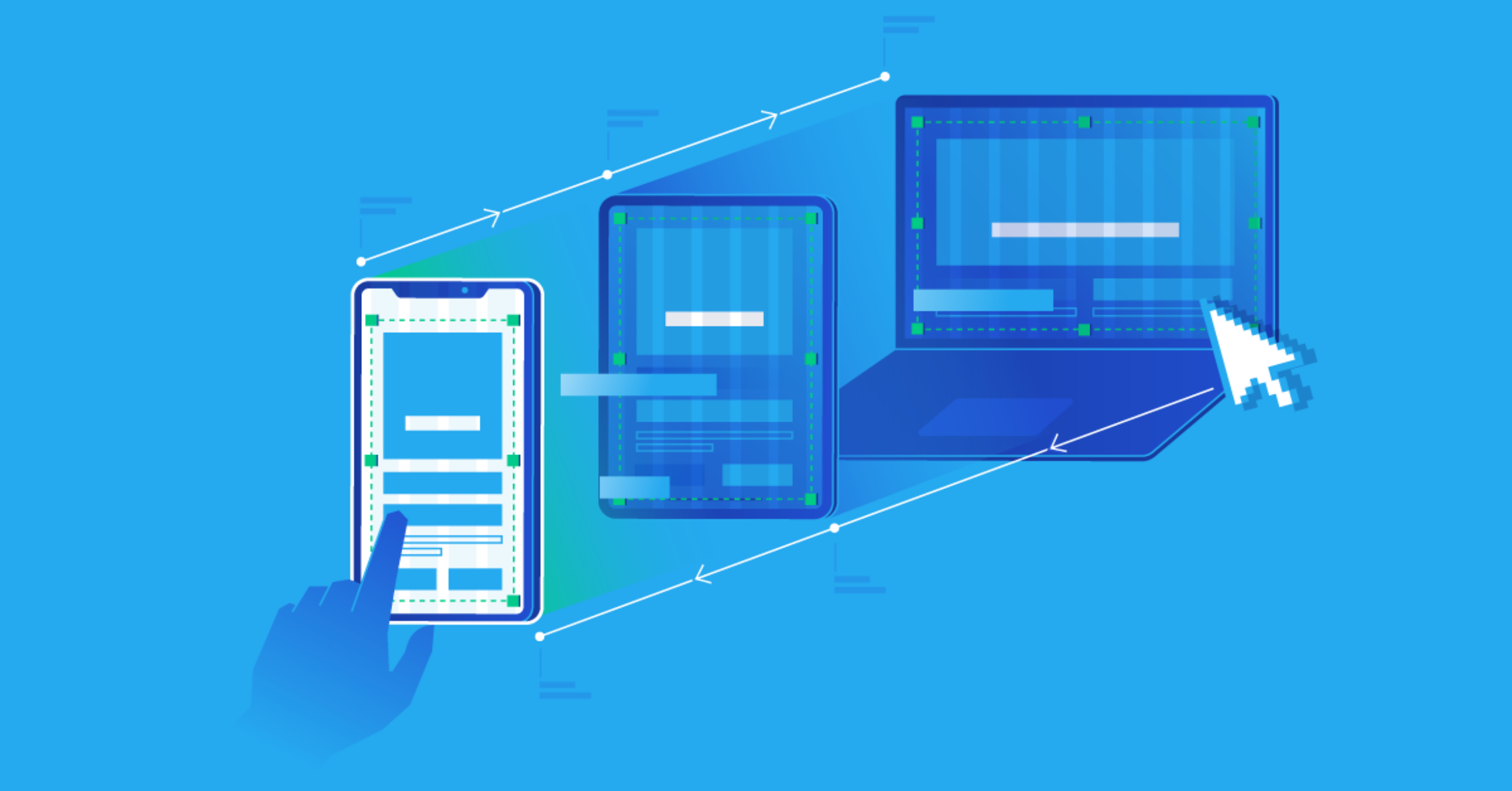
Responsive Design – Ensuring Websites Work on All Devices
In today’s digital world, people access websites using a variety of devices, ranging from large...
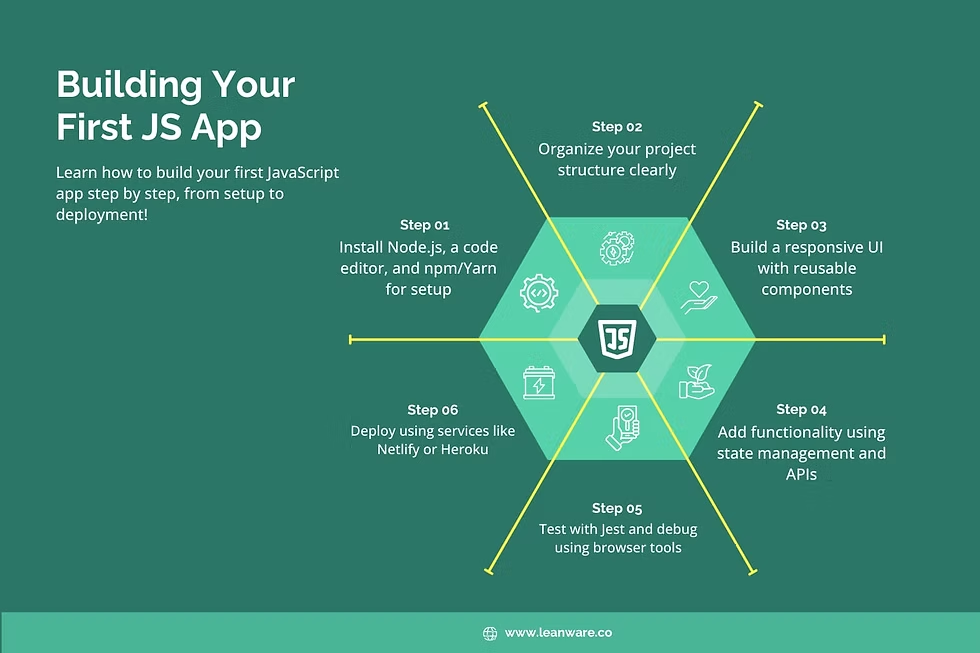
JavaScript – Adds Interactivity and Dynamic Behavior
In the modern world of web development, websites are no longer static pages of text and images...
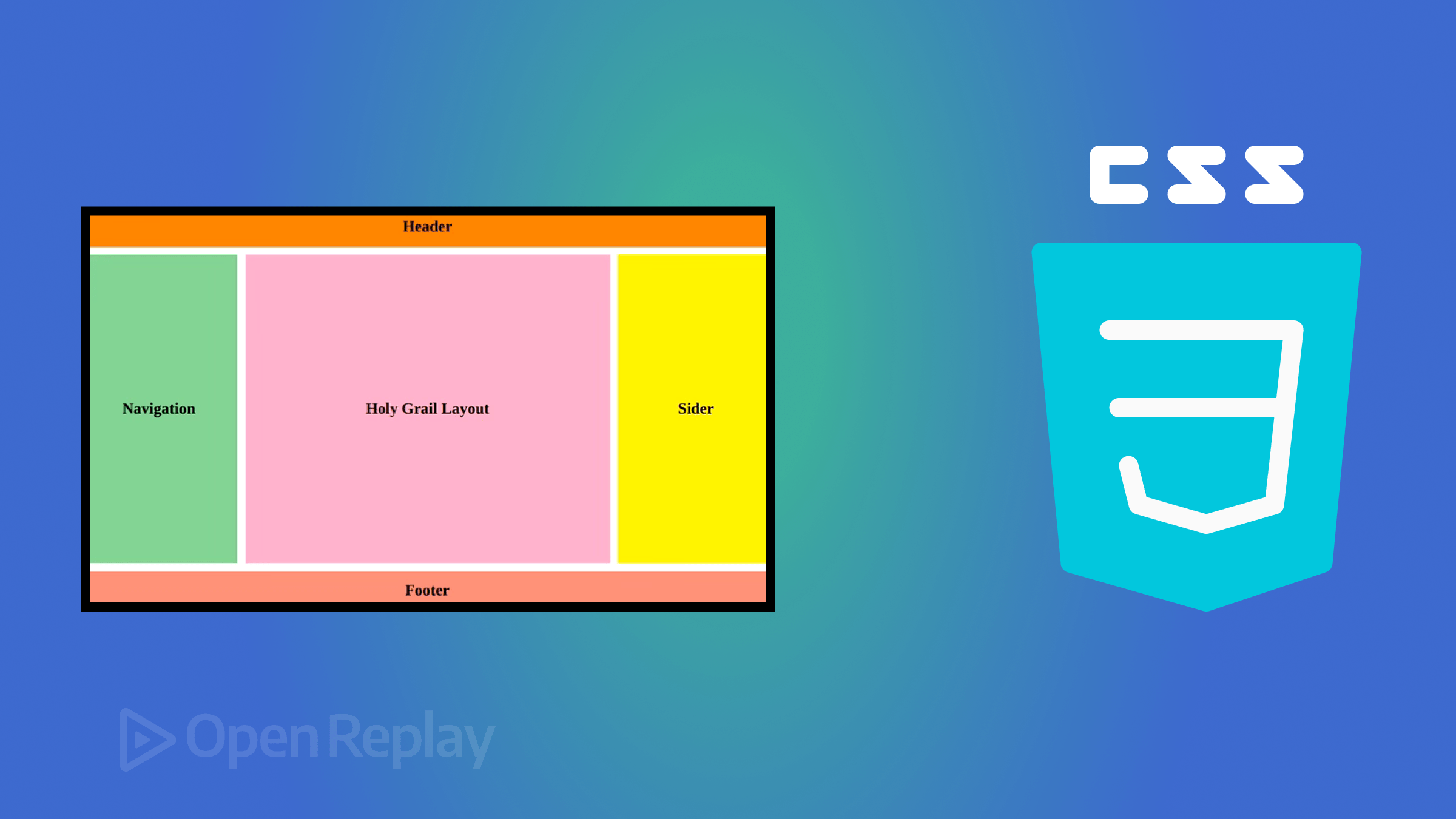
CSS – Styling and Layout of Websites
In the world of web development, creating websites that are both functional and visually appealing...
HTML – The Backbone Markup Language of Web Pages
The world of the internet is vast, complex, and dynamic. Every website you visit, from simple blogs...