In the world of web development, two terms are frequently mentioned: front-end and back-end development. These terms refer to different aspects of creating websites and applications, each with its own set of tools, responsibilities, and challenges. Understanding the difference between front-end and back-end development—and how they interact—is essential for anyone looking to dive into the tech industry.
What is Front-end Development?
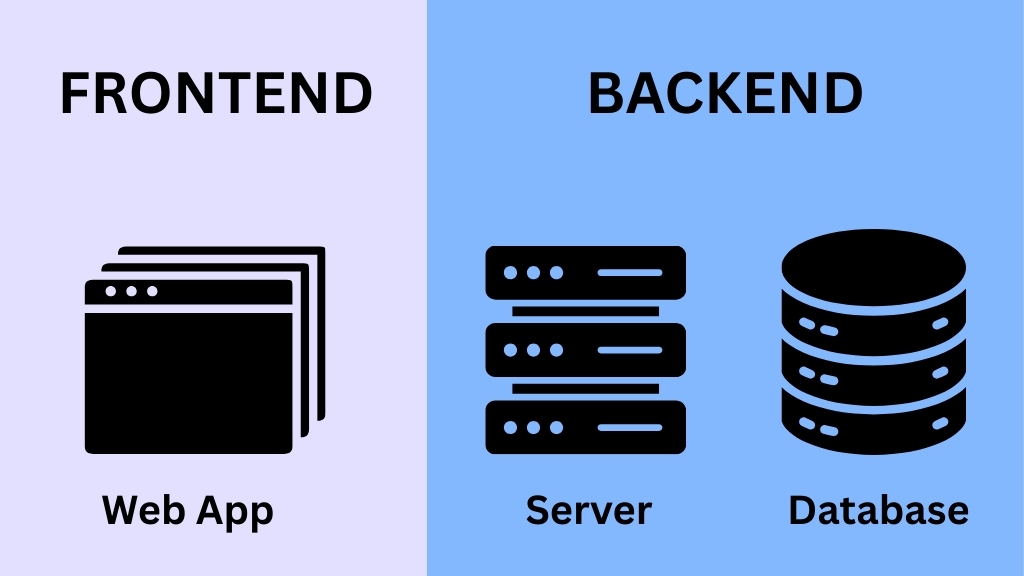
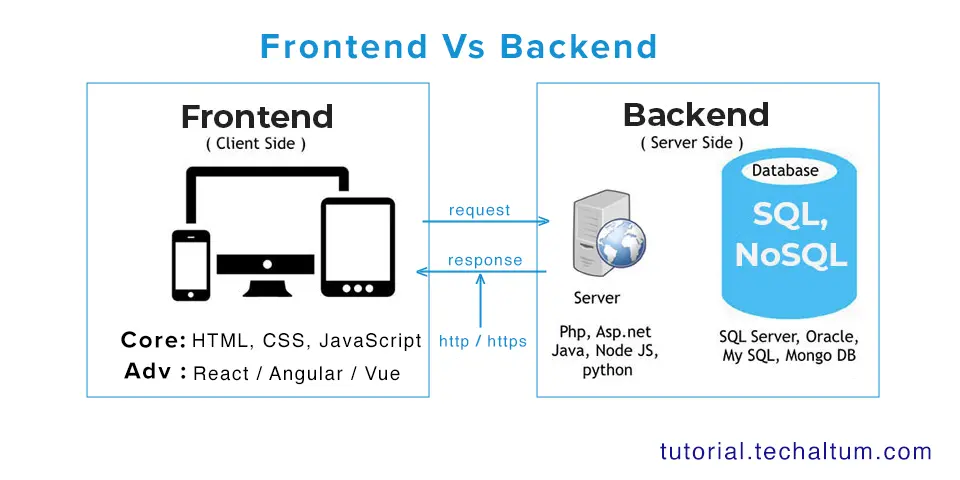
Front-end development, often called client-side development, refers to everything that users interact with directly in their web browser. The front-end is responsible for the visual layout, design, and interactivity of a website or web application. This includes elements like buttons, forms, text, images, navigation menus, animations, and responsive design.
Key Responsibilities of a Front-end Developer
Front-end developers focus on creating a seamless and user-friendly experience. Some of their main tasks include:
- User Interface (UI) Design – Ensuring that the website is visually appealing and easy to navigate.
- Responsive Design – Making sure that the website works well on all devices, including desktops, tablets, and smartphones.
- Performance Optimization – Ensuring that the website loads quickly and runs smoothly.
- Accessibility – Making the site usable for people with disabilities, following accessibility guidelines.
Common Front-end Technologies
Front-end developers rely on several core technologies:
- HTML (Hypertext Markup Language) – Provides the structure of web pages.
- CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) – Controls the visual presentation of the web page.
- JavaScript – Adds interactivity and dynamic behavior.
Modern front-end development often uses frameworks and libraries such as React, Angular, and Vue.js, which simplify the creation of complex user interfaces and improve development efficiency.
What is Back-end Development?
Back-end development, also known as server-side development, involves the part of the application that users cannot see. The back-end is responsible for managing data, handling requests, and ensuring that the website functions correctly. While front-end developers create the interface, back-end developers create the underlying logic that makes it all work.
Key Responsibilities of a Back-end Developer
Back-end developers focus on the functionality and logic behind the scenes. Some of their responsibilities include:
- Database Management – Storing and retrieving data efficiently and securely.
- Server Logic – Handling requests from the front-end and providing the appropriate response.
- Authentication and Authorization – Ensuring secure access to user accounts and data.
- API Development – Creating interfaces that allow the front-end and other applications to interact with the back-end.
Common Back-end Technologies
Back-end development relies on programming languages and frameworks such as:
- Python – Often used with frameworks like Django and Flask.
- JavaScript (Node.js) – Allows JavaScript to be used on the server-side.
- Java – Frequently used in enterprise applications.
- PHP – Common in web applications and content management systems.
- Ruby – Often used with the Ruby on Rails framework.
Back-end developers also work with databases, such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB, and Redis, to manage and store data efficiently.
Client-side vs. Server-side: Understanding the Difference
While front-end and back-end development are terms commonly used in the industry, they can also be described as client-side and server-side development.
- Client-side (Front-end) – Everything that happens in the user’s browser is considered client-side. It’s focused on how users see and interact with a website. For example, clicking a button that changes a menu layout without refreshing the page is handled on the client-side using JavaScript.
- Server-side (Back-end) – Everything that happens on the web server is considered server-side. This includes processing form submissions, retrieving data from databases, or sending emails. These operations are invisible to the user but are essential for a functioning website.
How They Work Together
Front-end and back-end development are interdependent. A well-designed front-end needs a reliable back-end to function, and an efficient back-end needs a user-friendly front-end to interact with. For example:
- When a user fills out a form on a website, the front-end handles the display and validation of the input.
- The back-end processes the input, stores it in a database, and returns a confirmation message.
- The front-end displays this confirmation to the user.
This seamless interaction is crucial for modern web applications.
Full-stack Development: Bridging the Gap
Some developers specialize in both front-end and back-end development, known as full-stack developers. They are capable of building an entire application from the user interface to the server logic and database management. Full-stack development is highly valued because it allows for more flexible and comprehensive solutions.
Key Skills for Front-end Developers
Front-end developers need both technical and design skills. Important skills include:
- Proficiency in HTML, CSS, and JavaScript
- Knowledge of front-end frameworks like React, Angular, or Vue.js
- Understanding of responsive and mobile-first design
- Familiarity with version control systems, such as Git
- Problem-solving and debugging skills
- Basic knowledge of UX/UI design principles
Key Skills for Back-end Developers
Back-end developers focus more on technical and logical skills. Important skills include:
- Proficiency in server-side languages like Python, Java, or Node.js
- Experience with databases (SQL and NoSQL)
- Knowledge of RESTful APIs and web services
- Understanding of server, network, and hosting environments
- Security practices and authentication mechanisms
- Debugging and optimization skills
Emerging Trends in Web Development
Web development is constantly evolving. Some emerging trends impacting front-end and back-end development include:
- Single Page Applications (SPAs) – SPAs use JavaScript to provide a smoother user experience by dynamically updating content without reloading the page.
- Serverless Architecture – Developers can build applications without managing servers, using cloud services to handle back-end logic.
- Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) – Web applications that behave like native apps on mobile devices.
- API-First Development – Building back-end APIs before creating the front-end to ensure smooth integration.
- Microservices Architecture – Breaking down the back-end into smaller, manageable services that can be developed and deployed independently.
Conclusion
Understanding the distinction between front-end and back-end development—or client-side and server-side development—is essential for anyone interested in web development. The front-end focuses on what users see and interact with, while the back-end ensures the application functions behind the scenes. Both sides are equally important and must work together seamlessly.
For those considering a career in web development, it’s valuable to choose a specialization or aim to become a full-stack developer. Each path has its own set of skills, tools, and challenges, but all play a vital role in creating modern, interactive, and reliable web applications.
Whether you are building a personal website, a complex e-commerce platform, or a dynamic web application, understanding the interplay between the front-end and back-end will help you create better user experiences and more efficient systems.